-
Running PET modules stand-alone
PET consists of several modules that can be run stand alone. These modules are written in C. The interaction of the different modules in shown in the figure. And the procedure can be summarized by the following steps:
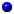 Extract the netlist from the layout (i.e. file [nle])
Extract the netlist from the layout (i.e. file [nle])
 Run PET analyze on the netlist [nle]
Run PET analyze on the netlist [nle]
 Add file [mon] to the input stimuli (generate file [csm])
Add file [mon] to the input stimuli (generate file [csm])
 Run COMPASS sim and obtain file [trc]
Run COMPASS sim and obtain file [trc]
 Run PET ttgen to generate file [trn]
Run PET ttgen to generate file [trn]
 Run PET calpot to calculate the power dissipation
Run PET calpot to calculate the power dissipation
analyze
analyze reads the extracted netlist and determines the output load for each cell of the circuit. It also provides to COMPASS sim the labels of the nodes to monitor. The files read are:- a configuration file (usually called .pet) containing general parameters such as: power supply voltage, clock frequency, time window of the simulation, reference to the standard cells library.
- the netlist [nle] extracted by COMPASS extract.
- a file containing the mapping of cell's pins for the library. Example.
The files produced are:
- a list of the nodes (file [mon]) to be monitored by COMPASS sim.
- the reference capacitance-node (file [cap]).
- the reference cell's output-node (file [acn]).
- the reference label-node (file [lab]).
All these references are resolved by calpot.
ttgen
COMPASS sim generates a simulation output file [trc] in tabular format. ttgen (transitions table generator) reads this file and create a transitions table [trn]. In this table each label/node is associated with the number of transitions occurred at that node during the simulation.calpot
calpot calculates the power dissipated in the unit under test. The files read are:- the three files generated by analyze: [cap], [acn], [lab].
- the transitions table file [trn] produced by ttgen.
- the configuration file .pet
- a file containing the values of energy-per-transition for each cell of the library. Example.
Power dissipation is given in mW (milli-watt).
ppcal
ppcal (partial power calculator) reads in a table in [calpot] format and computes the power dissipated by the unit (or sub-circuit) described by the table. The files read are:- the configuration file .pet
- the unit's [calpot] file.
The following modules are not directly involved in the power calculation, but are used to properly set up the working environment.
makePinLib
makePinLib (make pin library file) builds a file containing the mapping of output pins and the capacitance of the inputs for each cell of the library, from a more human readable description of the Standard Cell library. For more detail click here.mkmp
mkmp (make make-partial) reads a suitable [inst] file and generates an executable C-shell script as standard output. This script generates the partial calpot tables [calpot] for the instances contained in the unit under test. For more detail click here.
Copyright ©1996 Alberto Nannarelli,
All Rights Reserved. Last Modified: Jul 8, 1996
